Understand Your After Tax Returns With TaxDrag Metric

Harshith Sheggam
Understanding the Taxdrag Metric
When it comes to investing, the goal is often to maximize returns while managing risk. But one crucial factor that many investors overlook is the impact of taxes on their overall returns. Enter the taxdrag metric a concept that helps investors understand how taxes can reduce the effectiveness of their investment strategies.
In this blog post, we will dive into the taxdrag metric, explaining what it is, why it matters, and how investors can mitigate its negative effects.
What Is Taxdrag?
Taxdrag refers to the reduction in investment returns caused by taxes over time. When you invest, your portfolio earns returns in the form of dividends, interest, capital gains, and other income sources. Many of these returns are subject to taxation, and this tax burden can erode your overall investment performance.
For example, if you invest in a taxable account, your dividends and capital gains may be subject to income tax, reducing the net returns you receive. This tax burden can accumulate over time, especially if you frequently realize gains (i.e., sell investments for a profit) or receive taxable income from your holdings.
The taxdrag metric quantifies this reduction in returns due to taxes, helping investors understand how taxes are affecting their investment performance.
Why Does Taxdrag Matter?
Taxdrag matters because it can significantly impact your long-term wealth accumulation. Even small differences in tax treatment can have a compounding effect over time. To illustrate, consider two investors one who invests in a tax-efficient manner and another who pays higher taxes on their investments. Over time, the tax-efficient investor is likely to see better returns.
Taxdrag is particularly relevant in the context of:
- Investment accounts: Taxes on dividends, interest, and capital gains can reduce returns in taxable accounts, as opposed to tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs or 401(k)s.
- Active versus passive strategies: Actively trading stocks or other securities can trigger taxable events more frequently, leading to greater tax drag compared to a more passive strategy where investments are held for longer periods.
- Tax policies: Changes in tax rates or the introduction of new taxes can alter the impact of taxdrag on your investments. Understanding how to navigate these changes can improve your portfolio's after-tax returns.
How Is Taxdrag Calculated?
Calculating taxdrag involves estimating the effect of taxes on your portfolio's returns over time. This can be done in several ways, but the basic formula typically includes:
- Effective tax rate: This is the rate at which your investment returns are taxed, which can vary depending on the type of income (interest, dividends, capital gains) and the tax laws in your country.
- Portfolio turnover: The frequency at which you buy and sell investments in your portfolio. A higher turnover often results in higher taxes, as you realize more taxable events.
- Investment type: The type of investments you hold can also affect the taxdrag metric. For instance, bonds may generate taxable interest income, while stocks may yield dividends or capital gains. Some types of investments, like municipal bonds, may be exempt from federal taxes.
The taxdrag metric is typically expressed as a percentage of your overall return, indicating how much tax costs you in terms of lost investment growth.
FairShares to the Rescue
We understand that tax audits are typically conducted at the end of the year, and by that time, it’s too late to make adjustments to your tax savings. At Fairshares, we’ve recognized this challenge and are here to help you understand your tax drag metric every day.
We analyze your transactions regularly and calculate your tax drag metric, helping you stay on top of your tax situation throughout the year. Additionally, we calculate the tax drag metric on your unrealized gains, using the current or reference date’s fair market value price.
Why does this matter? By having a daily insight into your tax drag, you can better understand the after-tax impact of your investments. This empowers you to make informed decisions and be a smarter investor, with a clearer picture of your after-tax returns.
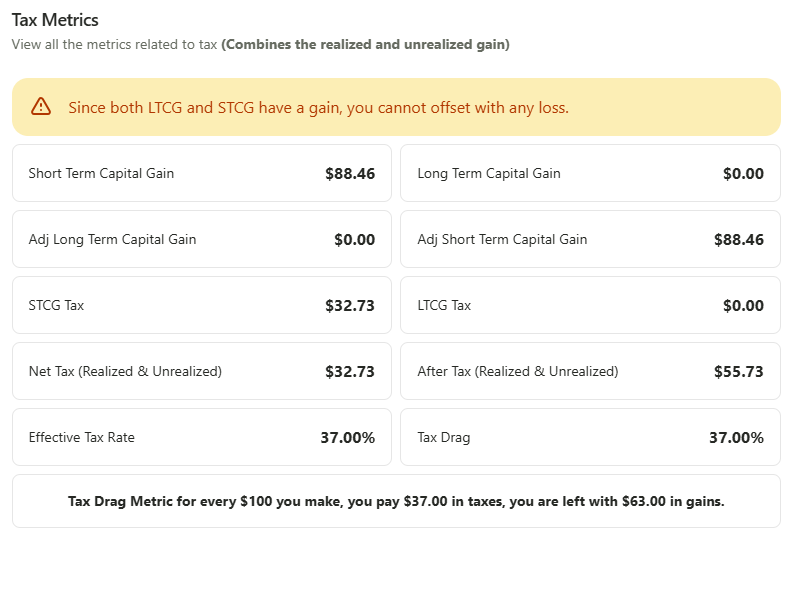
Understanding the after tax return with TaxDrag.
The basic concept to understand is that tax drag is simply the percentage of income reduced by taxes. However, to fully grasp tax drag, it's important to be aware of tax laws, as some securities are taxable while others are not. At FairShares, we simplify the process of calculating and tracking your tax drag metric.
Assuming the following.
- You have a gains(Both realized and unrealized) of $100.
- You have a Taxdrag Metric of 27%
For $100 in capital gains, you would earn 100 - 27% = $73. Your typical after-tax return would be $73.
NOTE: The tax drag metric does not represent your final after-tax return, it takes into account basic tax laws. On top of this, you may be eligible for additional tax benefits, which depend on various factors. For accurate tax returns, it is always advisable to consult a tax professional.
Ways to Reduce Taxdrag
While taxes are inevitable, there are strategies to reduce taxdrag and improve your investment returns:
Tax-efficient investing: This involves selecting investments that minimize taxable income. For example, focusing on tax-deferred accounts (like IRAs) or tax-exempt securities (like municipal bonds) can help reduce the tax burden.
Holding investments longer: The longer you hold an investment, the less likely you are to realize short-term capital gains, which are typically taxed at higher rates than long-term gains. A buy-and-hold strategy can lower the taxdrag on your portfolio.
Tax-loss harvesting: This strategy involves selling investments that have lost value in order to offset gains and reduce your taxable income. It’s a technique commonly used by active investors to reduce taxdrag.
Asset location: Strategically placing assets in the most tax-efficient accounts can reduce taxdrag. For example, holding income-generating investments like bonds in tax-deferred accounts, while keeping growth-oriented investments like stocks in taxable accounts, can minimize the tax impact.
Consider tax-advantaged accounts: Contributing to tax-advantaged accounts like IRAs, 401(k)s, or Roth IRAs allows investments to grow without immediate tax implications, helping you to avoid taxdrag.
FairShares to the Rescue Again.
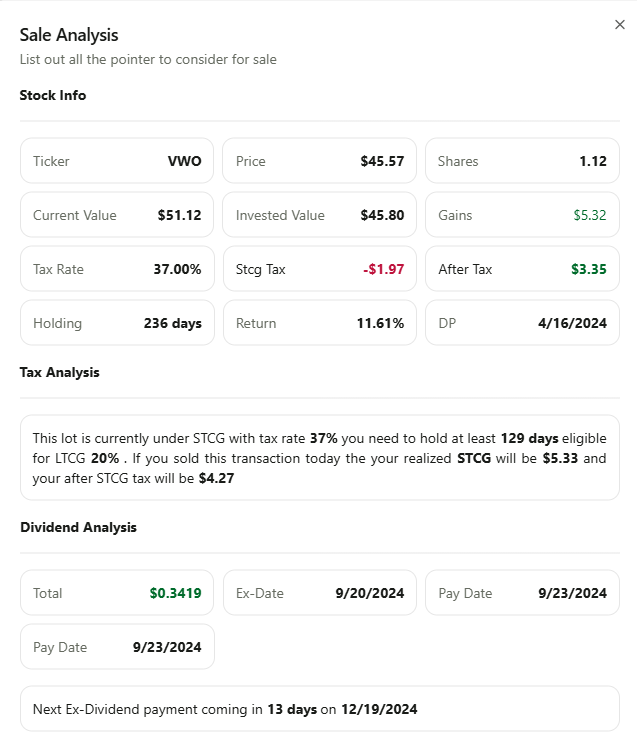
FairShares offers a metric called Sale Analysis,This is on tax lot level. which helps you understand your tax obligations. This Analysis provides insights into whether your gains are subject to long-term or short-term capital gains tax, and whether it's beneficial to wait for long-term treatment to reduce your tax liability. It also alerts you about upcoming dividend payments, suggesting whether you should hold off on selling, or warns you if you're at risk of a wash sale. Essentially, this metric helps you make informed decisions to minimize your tax burden.Again we are not influencing your decision on buying or sell we are helping to understand your tax obligation.
Conclusion
Taxdrag is a critical metric that every investor should be aware of. It measures the impact of taxes on your investment returns and can significantly affect the long-term growth of your wealth. By understanding how taxes reduce your returns, you can take steps to mitigate taxdrag and maximize the after-tax value of your investments.
Incorporating tax-efficient strategies like asset location, tax-loss harvesting, and holding investments longer can reduce the drag taxes impose on your portfolio. Ultimately, a tax-conscious approach to investing can help you keep more of your returns, contributing to your long-term financial success.
This blog post provides a comprehensive explanation of taxdrag, its importance, and ways to reduce it, offering valuable insights for investors looking to optimize their portfolios.
